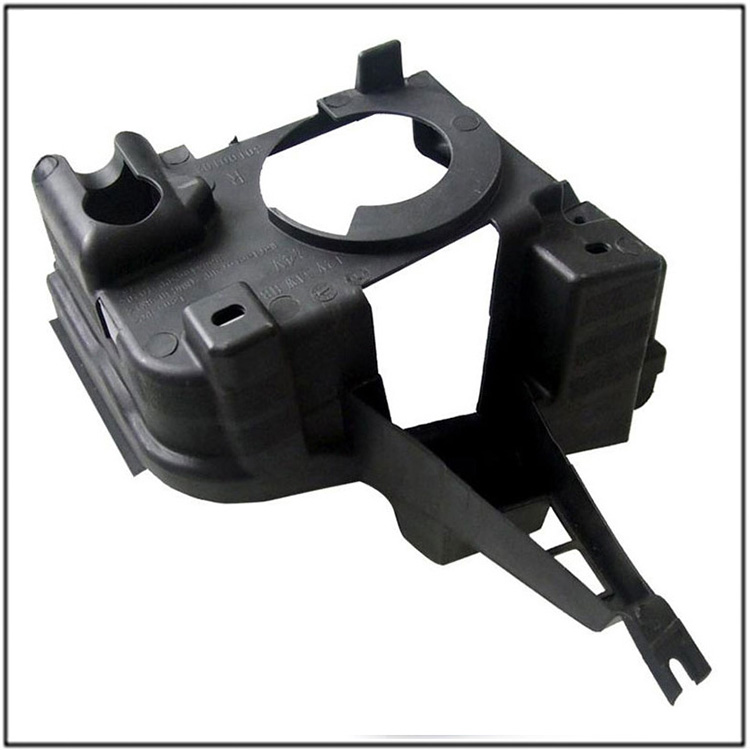
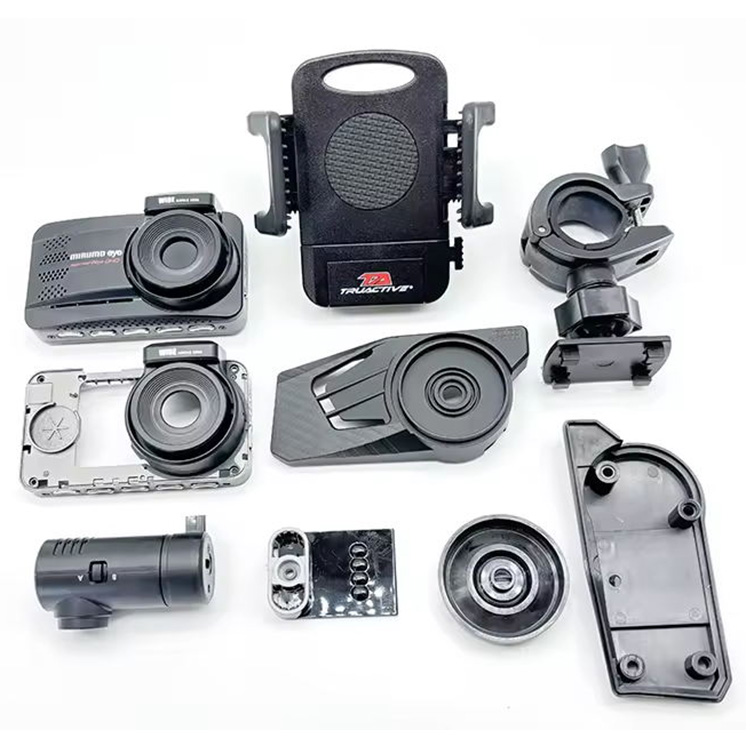
What are The Four Stages of Injection Molding?
Customers often ask me how the injection molding process is carried out. It's actually quite simple.
The four stages are clamping, injection, cooling, and demolding. Each step can perfectly shape plastic.
I have been engaged in these stages for 20 years. They are crucial. Do you want to know how complex it is?
As long as the equipment and personnel are in place, it's not difficult. Precision equipment and skilled workers can ensure smooth processes.
Phase 1: When the screw pushes molten polymer into the mold cavity at a pressure exceeding 150 MPa, the material undergoes its first phase transition from viscoelastic to solid prototype. The essence of this stage lies in the dynamic control of the melt front - too fast a flow rate can induce turbulence leading to gas marks, while too slow a propulsion can cause cold material condensation. Modern injection molding optimizes the 0.8mm thin-walled area of car lampshades with 4mm reinforcing ribs through multi-stage injection curves, and compresses the temperature difference at the flow front to within 3 ℃. The spreading trajectory of the melt in the mold cavity is essentially a solidification map drawn between the gaps of viscous resistance and thermal conduction.
The second stage: the pressure holding stage that switches instantly when the mold cavity is filled, is the key battle that determines the product density in injection molding. At this point, the melt enters a special state where non Newtonian fluids coexist with solidified crystal nuclei, and the screw continuously applies a pressure of 30-80 MPa to compensate for shrinkage. In the molding of medical syringe barrels, for every 10 MPa increase in holding pressure, the crystallinity of polypropylene increases by 7%, directly affecting puncture toughness. Even more ingenious is the timing control: a 0.5-second pressure holding delay may cause the gate to freeze, causing the volume shrinkage rate of the connector socket to fluctuate by more than 12%. The intelligent injection molding unit constructs a real-time pressure field cloud map of the mold cavity through a pressure sensor network, dynamically adjusts the compensation curve, and locks size fluctuations in a micro cage of ± 0.02mm.
The third stage: the cooling stage, which accounts for 70% of the entire cycle, is an efficiency revolution dominated by heat conduction. When the cooling water flushes the waterway in a turbulent state, the thermal conductivity of the mold steel and the specific heat capacity of the plastic part are jointly written into the solidification equation. In the injection molding of a laptop shell, reducing the cooling water temperature from 25 ℃ to 15 ℃ can shorten the demolding time of ABS by 40%, but excessive temperature difference can induce internal stress. The cutting-edge temperature control technology improves cooling efficiency by 55% while ensuring dimensional stability by dynamically adjusting the mold temperature (within the range of 30-120 ℃). This thermal management art allows the injection molding process to control the spectrum from liquid carbon fiber PPS to ultra flexible TPE.
The fourth stage: The moment when the ejector pin contacts the plastic part is the most fragile mechanical critical point in injection molding. At this point, the product is near the glass transition temperature (Tg), and a 0.01mm ejection eccentricity may cause deformation of the micro gear teeth. The car filter housing adopts a nitrogen assisted ejector system, which uniformly applies pressure through 72 micropores to achieve a demolding stress distribution uniformity of 98%. The more advanced phase change intelligent top rod can switch from rigid to elastic mode at the moment of contact, eliminating top white defects while increasing the qualification rate of thin-walled parts to 99.9%.
These four stages are evolving into autonomous optimized digital twins. Quantum computing driven thermal conduction simulation compresses the prediction error of cooling time to 0.3 seconds; A self-learning system for ejection trajectory based on computer vision enables molds to have adaptive capabilities to cope with material aging. From the 0.2mm micro column array of medical microfluidic chips to the 8-meter skeleton of wind turbine blades, the injection molded quartet evolves synchronously at the micro and macro scales - it is not only a faithful executor of physical laws, but also an innovative carrier that breaks through material limits.