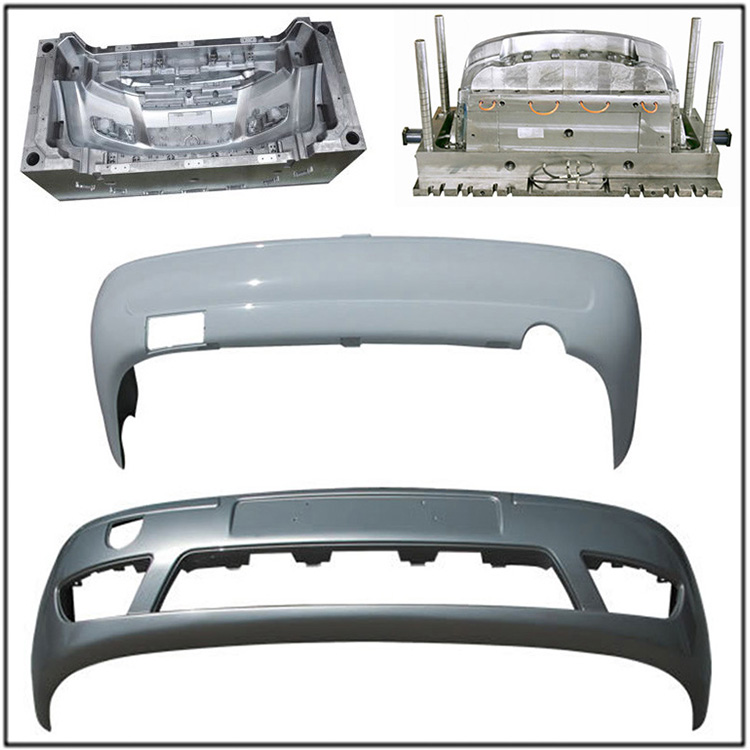
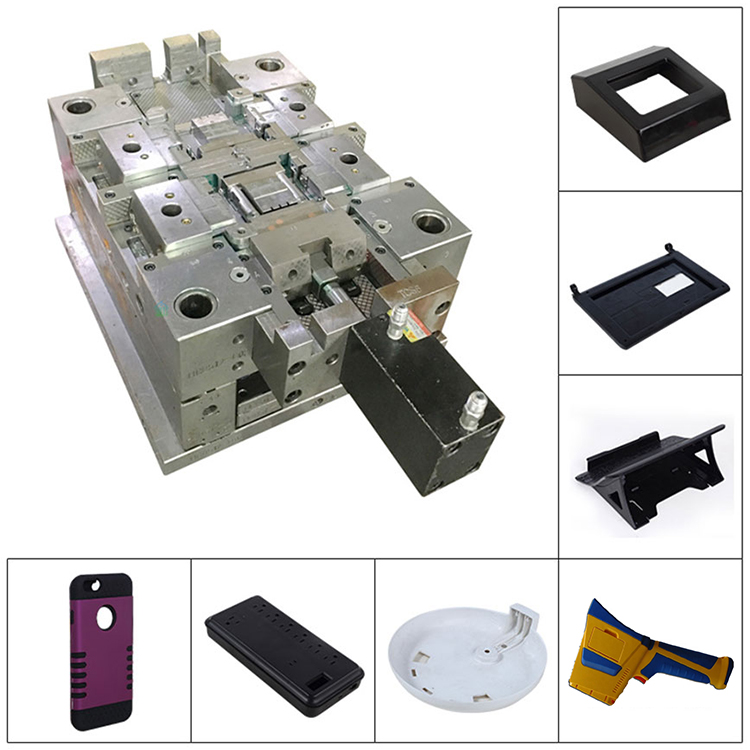
How to Eject The Product Out Of The Threaded Mold Push Plate?
In the design of threaded molds, the push plate system is a key component to ensure smooth demolding of the product. Due to the special nature of the threaded structure, traditional ejection methods often cannot meet the requirements, so the design of the push plate system needs to be more precise and clever. So, how does the thread mold push plate push out the product? Let's analyze this process in detail from structure to operating principle!
Firstly, the push plate system of the threaded mold mainly consists of three parts: the push plate, the ejector pin, and the threaded core. The push plate is usually installed on the moving part of the mold, and the ejector pin is fixed on the push plate. When the mold is opened, the ejector mechanism of the injection molding machine will push the push plate forward, and the ejector pin will then push the product out of the mold cavity. However, for products with threaded structures, relying solely on push plates and top pins is not enough, and the cooperation of threaded cores is also required to complete demolding.
The threaded core is the core component of the push plate system, usually installed in the fixed part of the mold. It is equipped with a rotating mechanism inside, which can be driven by gears, chains, or hydraulic motors. During the mold opening process, as the push plate moves forward, the threaded core begins to rotate. This rotation action gradually separates the threaded part from the product, avoiding thread damage or product deformation caused by forced ejection. The rotation speed of the threaded core and the movement speed of the push plate need to be accurately matched to ensure a smooth and smooth demolding process.
In practical operation, the ejection action of the push board system is divided into several steps. Firstly, after the injection molding machine completes injection molding and maintains pressure, the mold begins to open. At this point, the push plate moves forward under the push of the ejector mechanism, and the ejector pin begins to contact the product. At the same time, the threaded core begins to rotate through the transmission system. The movement of the push plate and the rotation of the threaded core are synchronized. The push plate is responsible for pushing the product out of the mold cavity, while the threaded core gradually disengages the threaded part from the product through rotation. This collaborative action ensures that the threaded part can be smoothly demolded while avoiding product damage.
The design of the push plate system also needs to consider the structure and material characteristics of the product. For products with deep or fine threads, higher precision is required for the fit between the push plate and the threaded core. Usually, the surface of threaded cores is treated with special treatments such as chrome plating or nitriding to improve wear resistance and reduce friction. In addition, the materials for the push plate and ejector pin also need to have high hardness and wear resistance, and commonly used materials include SKD61 and SUJ2.
In actual production, maintenance of the push plate system is also very important. Regularly checking the wear of the push plate, ejector pin, and threaded core, and promptly cleaning dust and impurities can effectively extend the service life of the mold. If the threaded core or ejector pin is found to be severely worn, it should be replaced in a timely manner to avoid affecting product quality.
In summary, the thread mold push plate pushes the product out of the mold through the collaborative work of the push plate, ejector pin, and thread core. The movement of the push plate and the rotation of the threaded core need to be precisely synchronized to ensure that the threaded part can be smoothly demolded. Reasonable design, precise machining, and regular maintenance are the key to the efficient operation of the push plate system.